Introduction:
I didn't start my career with java, but with python and a bit of C. Then years after, I am learning java for android projects. In this blog, I will point out how I am learning java and also a little bit of resources and information along the way to help you learn.
This is more for a person who already is familiar with the programming concepts but is getting accustomed with the java syntax. Also it only spans to very basic and if people like it then only I will proceed with further details. I have taken guidance and screenshots from the android course by rob percieval for this blog. If you want to learn android, do take his course.
Thanks and lets begin.
Initial observations:
(1) a java code needs to have a class to start with. Also each class has method or functions associated to a class. among these methods, it must have the main method.
(2) void means it returns nothing.
(3) static means some variable which doesn't change at all. it is only dependent on the class, and not on the instance. which also means that it will be same across instances and can't be changed.
(4) println stands for print a line.
Data types: primitive and derivatives:
primitive types are char, int, double, boolean, byte, long and short. these are the similar types we use in c, c++ or any other similar strong typed language. java is also a strong typed language, hence all the types.
But String myname = 'rob';
this assignment has string starting with capital letter as string is not a primitive type. 'String' is a char array, and it is actually a class in java. Also, java allows string concatenation simply, just like python. for example, look at this little example below:
also, primitives like int can be implicitly converted while printing unlike python or javascript. for example look into this below:
also, we can call methods of a class, even the simple ones also; just like we do in python. see how we use length() of a string using this process:
a simple task involving all the variables:
Arrays in java:
seems like that java uses curly bracket to write array. also you can't directly print this. But good thing again is that it uses 0 to start indexing.
simple array is unmutable. so you can't change them.
for using list in java, we need to import java.util.* to use all the java items. Now, we can use list by using ArrayList().
so it will work like this:
List listName = new ArrayList();
simply add is the method for adding items.
listName.add(1); listName.add(2); so on.
list.get(index_no) gives you the index_no element from the list.
list.remove(index_no) is a pop from python.
list.toString() is also good.
a small task:
so basically, Arraylist() is the type. add is the new append. remove is the pop. and get is for getting specific index. tostring is a method not there in python ( at least I don't know of).
oh before we move on, java, doesn't take or I will say accept single quotes. strings are not defined in java with single quotes. I find it weird but maybe that's how it is.
Dictionaries in java:
Map map = new HashMap();
Map.put(father, "rob");
also Map allows Map.size() telling you the length of it.
Map.toString() lets you print it.
Map.remove('key') lets you remove a specific key. Basically an equivalent to del Map['key']
Rob didn't provide any tutorial for map procedure.
Now we will be learning conditionals.
If
simple if works in the following syntax:
if(condition) { //code block}
if else works in the following syntax
if(condition){//code block}else(condition){//code block}
Now, rob gave a simple task here. create a list of two integers; and then compare them and print which one is bigger.
I tried it with ArrayList but failed. It seems that I struck an error named
java.lang.object is bad operand for >
But why does this occur?
this occurs because arraylist elements are non-primitive. and you can't do operator overloading in java like in python; so you would have to use something called comparable.
A detailed description of it is provided here.
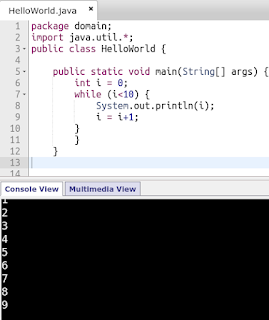
Next up: while loop:
syntax:
while(condition){code}
please consider for this type of loop that it surely ends. otherwise you would keep looping for infinite and crash browser/laptop/ide etc.
Sure. Now, let's see more.
We will try the simple "print the even numbers" question which rob gives as assignment.
interesting fact x++ works in java too. i.e. the "++" increment. So questions related to x = x+1 and x++ problems can be asked too for java interviews.
For loop:
for loop is exactly similar to the c format. the syntax is:
for(datatype variable = startpoint; variable endpoint condition; variable -- or ++) {codeblock}
see this block of code in action.
A bit more complicated example, where we solve the task given by rob to solve triangular numbers.
Conclusion:
So that's it. We are done with the basics, i.e. data types, conditionals and dictionary, list etc. Next is learning specific coding techniques and oops tricks to java; which you can start on your own. Let me know in the comments what more would you like to read about java and or specific concepts etc. Thank you for reading and stay tuned to the blog.













Comments
Post a Comment